
Suppose the internal penetration tester is able to extract cleartext credentials from memory or crack the collected hashes, they will be able to authenticate across additional network resources and services such as Outlook, business-critical web applications, and device portals, amongst many others.
WDigest Authentication is a challenge/response protocol that was primarily used for LDAP and web-based authentication in Windows Server 2003. It was introduced for the first time in Windows XP and was enabled by default on Windows systems. It allows clients to communicate cleartext credentials to Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Simple Authentication Security Layer (SASL) applications.

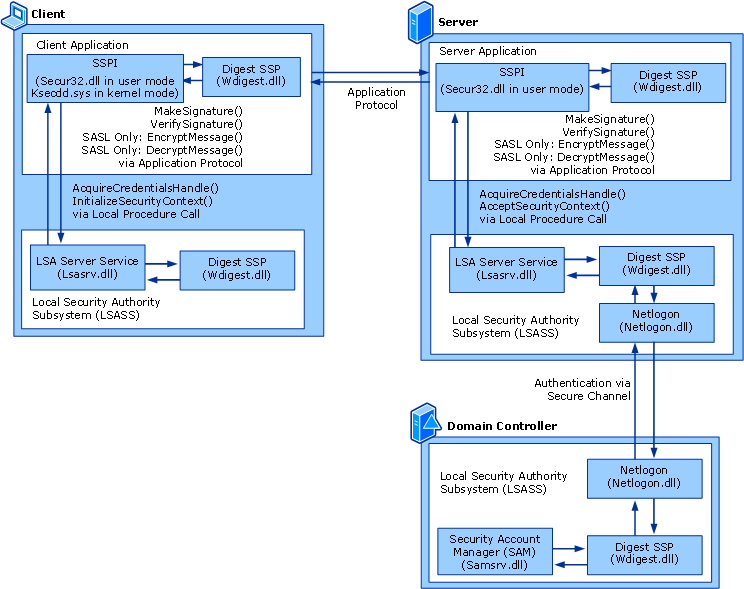
These exchanges require that parties that seek to authenticate must demonstrate their knowledge of secret keys. Microsoft cached the cleartext credentials in Windows RAM when users logged in to their workstations to make the authentication procedure more convenient for end users. Workstations used these cached credentials to authenticate HTTP and SASL services without requiring users to enter their credentials over and over again. The cleartext credentials authenticate via HTTP and SASL exchanges.
For example, a client requests access, the authenticating server challenges the client, and the client answers by encrypting its response with a key derived from the password. To ascertain if the user has the right password, the encrypted response is compared to a previously stored response on the authenticating server.
🚫**This is where the crux of the problem resides!**🚫